Scope of Applications
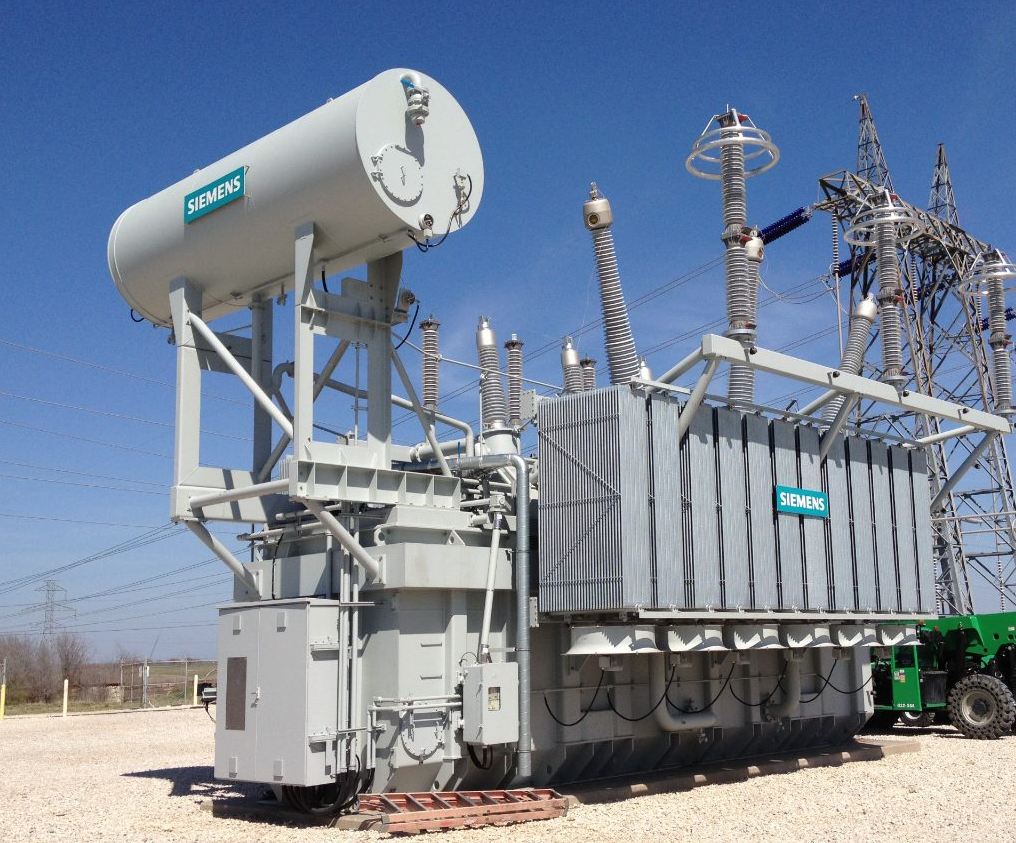
We offer a variety of different products. In order to provide you with an overview of the respective application areas,
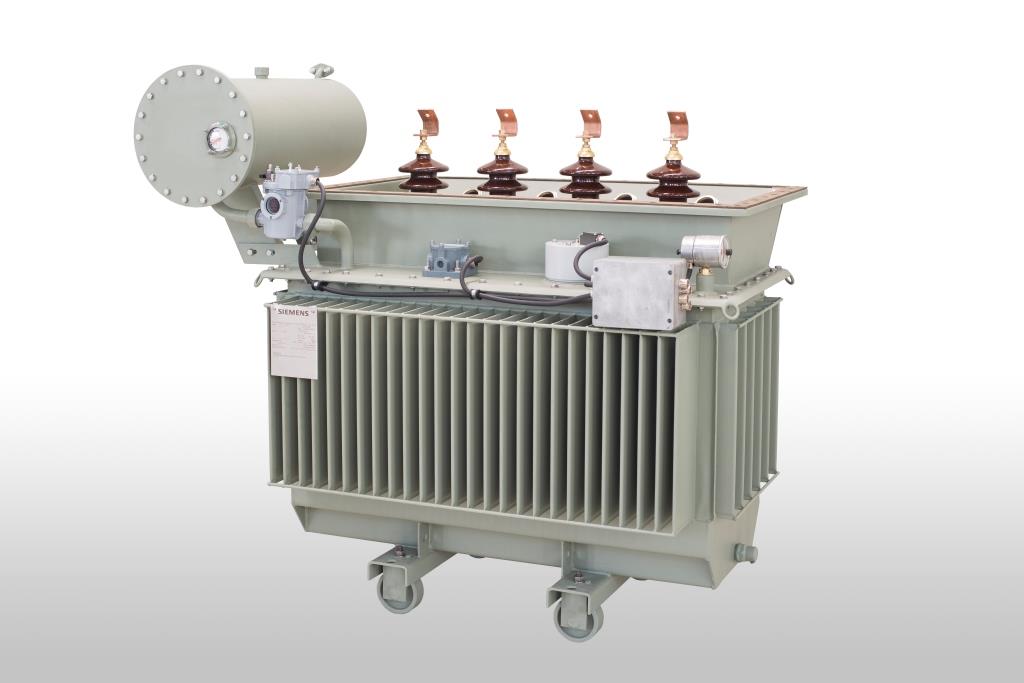
you will find below our products matchd with respective transformer type. Discover our product portfolio by moving your mouse over the markings on the transformer image.
If you are interested in one of these products in particular, you can simply click on the open image and go to the respective product page.
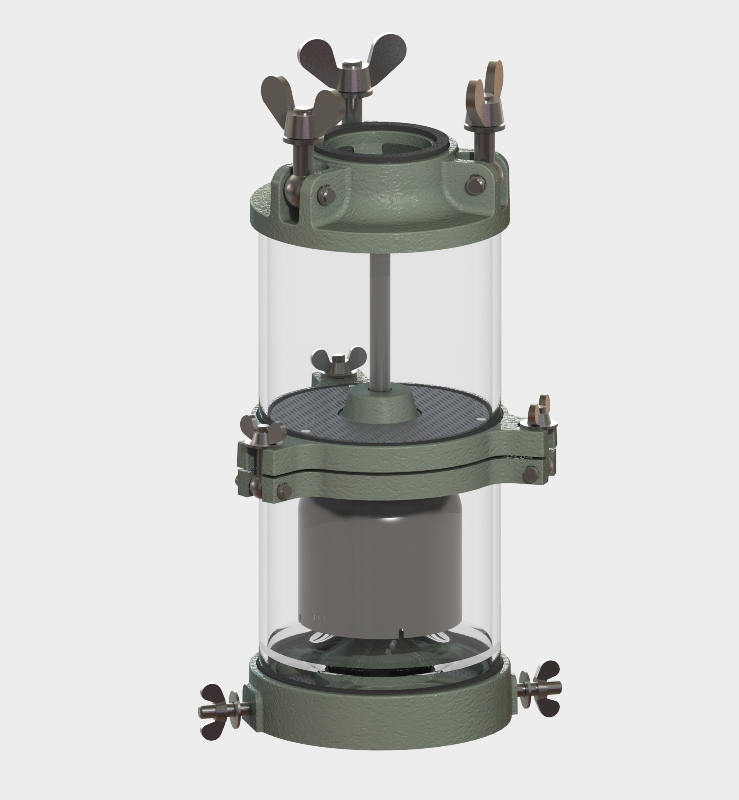
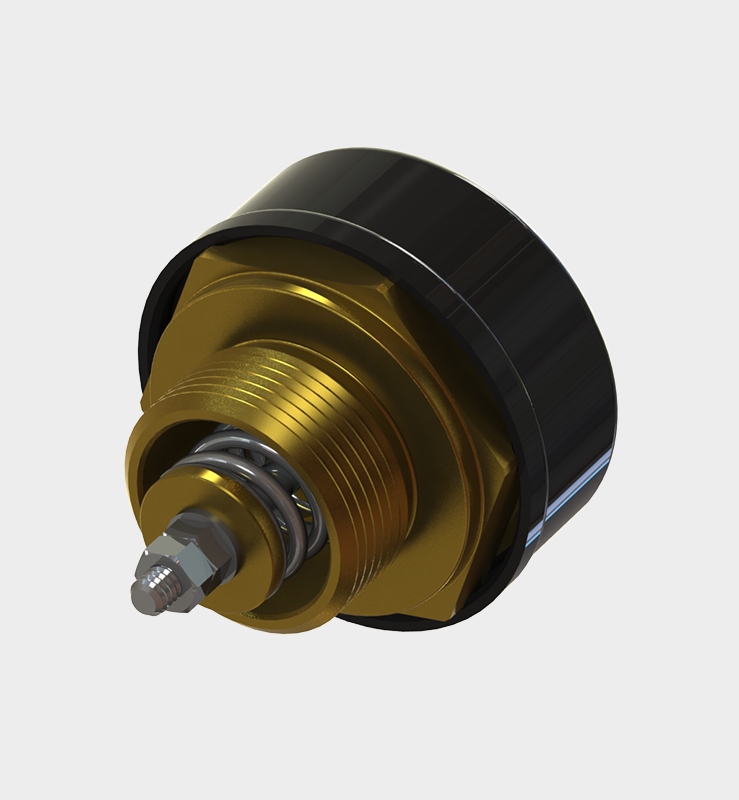
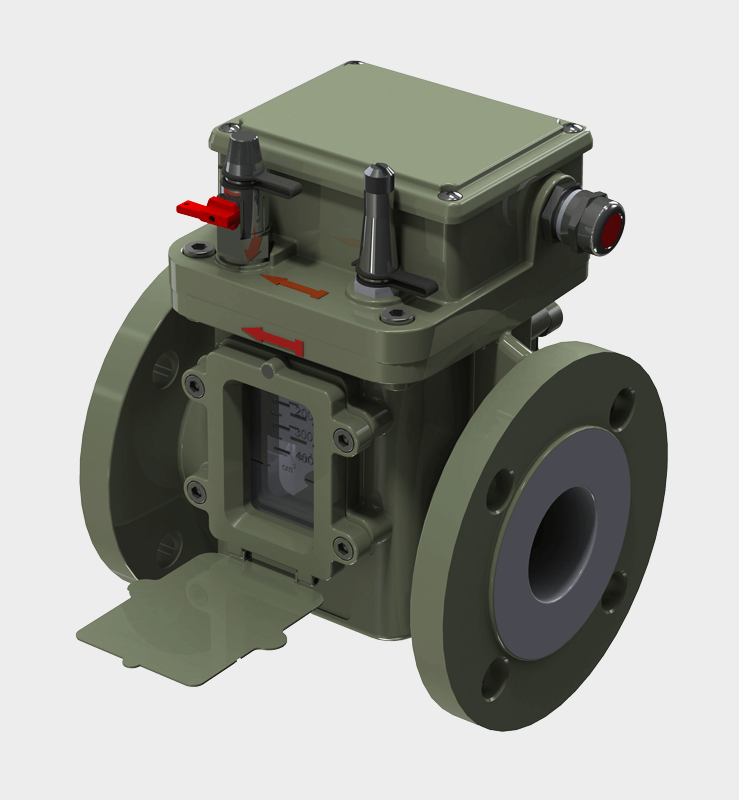
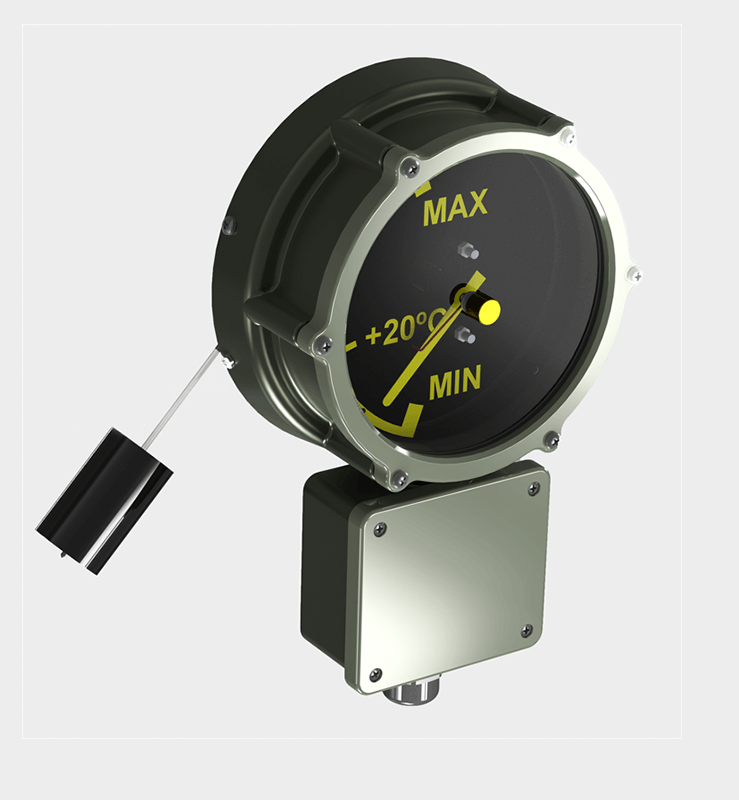
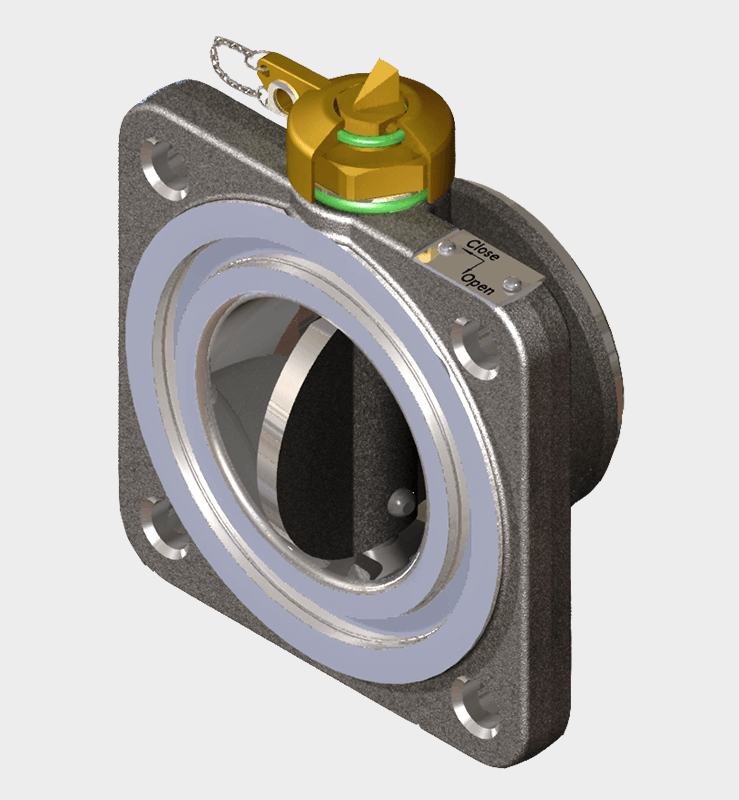
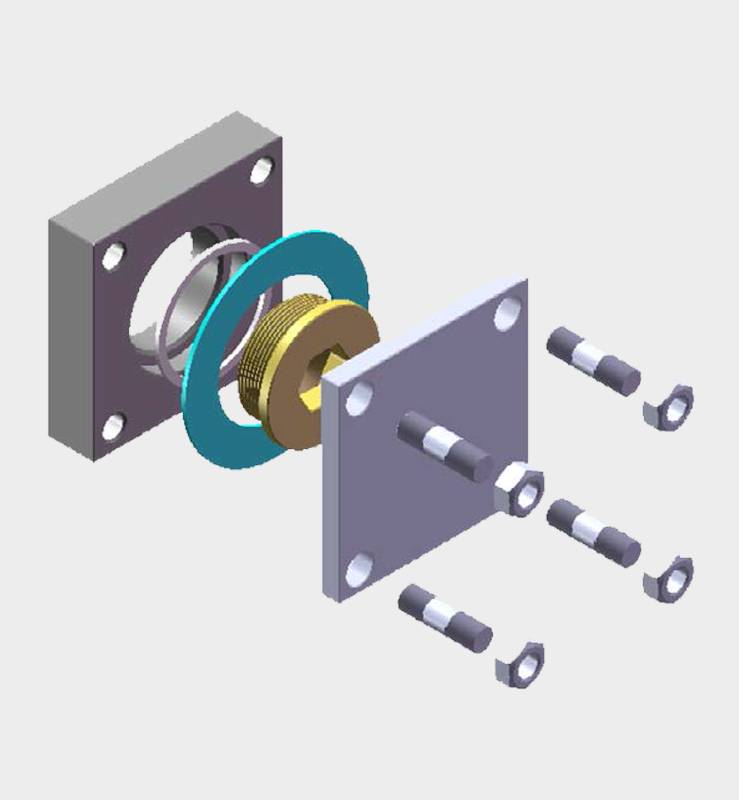
Our main products include the welding neck flange radiator valves in accordance with DIN 42560 type A, the wafer type radiator valves according to DIN 42560 form B as well as our new protective devices such as Buchholzrelais MBP and the hermetic protection device MCHD. Many more of our products can be found on the respective product pages.
Power transformers
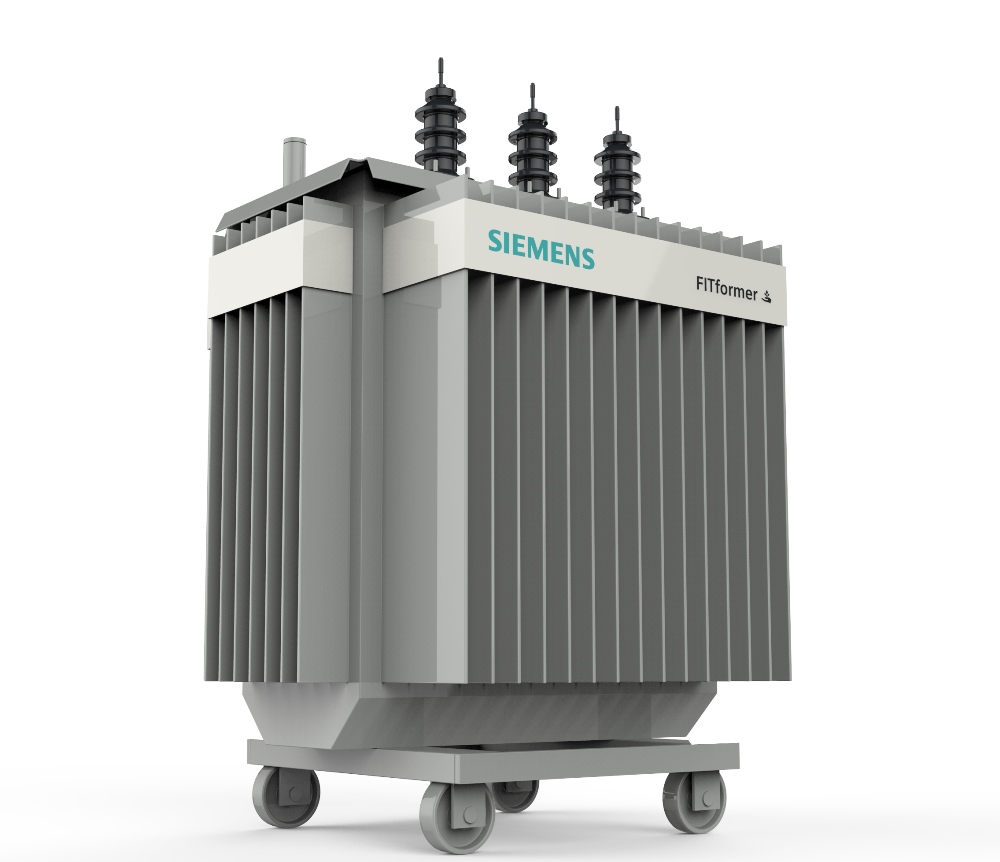
Hermetically sealed distribution transformers
Distribution transformers with expansion tank
How does a transformer work
A transformer is mainly used in the power supply for current transmission. They serve to convert an input AC voltage into an output AC voltage in a circuit. The transformer consists of at least two copper windings arranged side by side on an iron core.
The conversion ratio corresponds to the number of windings of the input coil (primary side) in relation to the winding number of the output coil (secondary side).
The principle of the transformer was discovered in the 1830 years, but the first transformer was developed only 50 years later. In the meantime there are power transformers from 30 to over 1300 MVA. In order to be able to transport electricity over long distances, different transformers are used depending on the requirements. A distinction is made here between power transformer, distribution transformer and HVDC (high-voltage direct-current transmission).